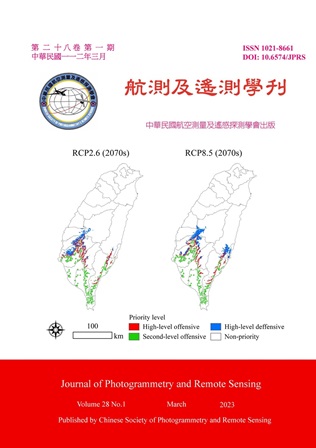
Climate change may drive the range expansion of invasive species. Integrations of spatially explicit information are useful for preventing and managing. In this study, we used MaxEnt and MigClim modelling approaches to map current and future distribution dynamic of the invasive plant, Mimosa diplotricha. Then, structural and functional connectivity was integrated to develop the prevention strategies under climate change scenarios. The results showed that the suitable niche of M. diplotricha was a warm environment with the large variation in day-night temperature. The range of this species may increase due to a warming climate, with future expansion to the north of current suitable habitats. However, the critical routes of dispersal is likely to vary with the degree of warming. In conclusion, regardless of the warming scenario, the northern edge of the present habitat should be prioritized for control. In addition, as the warming increases, more attention should be paid to the defense of invasion risk areas in the future.